
FREE IN HOME ESTIMATE!
 |
What Causes Indoor Air Problems? Indoor pollution sources that release gases or particles into the air are the primary cause of indoor air quality problems in homes. Inadequate ventilation can increase indoor pollutant levels by not bringing in enough outdoor air to dilute emissions from indoor sources and by not carrying indoor air pollutants out of the home. High temperature and humidity levels can also increase concentrations of some pollutants. |
|
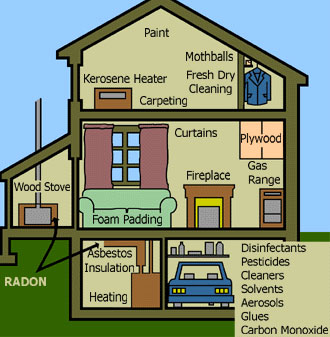 |
Pollutant Sources There are many sources of indoor air pollution in any home. These include combustion sources such as oil, gas, kerosene, coal, wood, and tobacco products; building materials and furnishings as diverse as deteriorated, asbestos-containing insulation, wet or damp carpet, and cabinetry or furniture made of certain pressed wood products; products for household cleaning and maintenance, personal care, or hobbies; central heating and cooling systems and humidification devices; and outdoor sources such asradon, pesticides, and outdoor air pollution. |
|
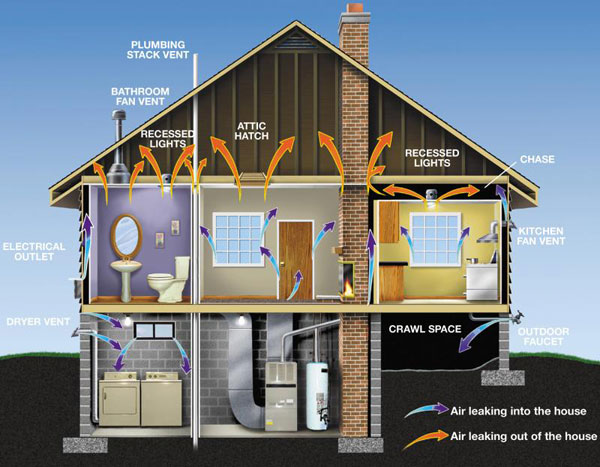
How Does Outdoor Air Enter a House? Outdoor air enters and leaves a house by: infiltration, natural ventilation, and mechanical ventilation. Outdoor air flows into the house through openings, joints, and cracks in walls, floors, and ceilings, and around windows and doors. Air can move through open windows and doors, from fan powered vents. |
||
 |
||
Amount of Ventilation If too little outdoor air enters a home, pollutants can accumulate to levels that can pose health and comfort problems. Unless they are built with special mechanical means of ventilation, homes that are designed and constructed to minimize the amount of outdoor air that can "leak" into and out of the home may have higher pollutant levels than other homes. |
||

